A. Student Lead Seminar on Populations and Samples
B. Statistical Hypothesis Testing
C.
Characteristics of Good/Bad
Models; Bivariate Models and
D. Key Concepts: economy; parsimony; skewness; kurtosis; independence;
linear relationship; chi-square; observed versus expected; degrees of freedom;
Fisher exact test; Pearson correlation; linearity; homoscedasticity; Ho,
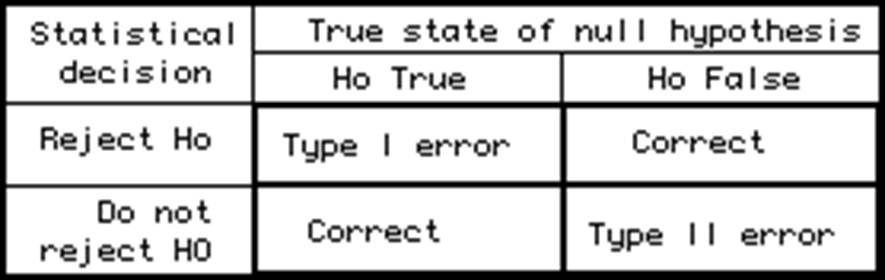
H1 or HA; Type I and Type II errors; alpha or beta errors
E. Key and Classic Readings:
1.
J. P. Guilford, Fundamental Statistics in Psychology and Education
, 3rd ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1956), p. 145 for
five terms for interpreting correlation statistics:
a) slight (<.20),
b) low (.20-.40),
c) moderate (.40-.70),
d) high (.70-.90), and
e) very high (>.90).
2.
John V. Richardson, Jr. “Good
Models of Reference Service Transactions: Applying Quantitative Concepts to
Generate Characteristic Attributes of Soundness,”
The Reference Librarian (April 2009):
159-177.
Updated:
24 February 2014.